

Understand Urticaria and How to Regain Healthy, Comfortable Skin
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition marked by sudden, itchy red or pink welts that can appear anywhere on the body. These welts may vary in size and shape, sometimes merging to form larger patches, and can be triggered by allergies, infections, stress, or environmental factors. While urticaria is usually temporary, recurring or chronic cases can disrupt daily life and affect confidence. In this guide, we explore the causes, symptoms, and professional treatments for urticaria, helping you take the first step toward calm, healthy, and comfortable skin.
Patients Treated
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body. These raised patches vary in size and shape and occur when the immune system releases histamine, causing fluid to leak into the skin. While hives can last from a few minutes to several weeks, recurring or severe episodes can significantly affect daily life and comfort.
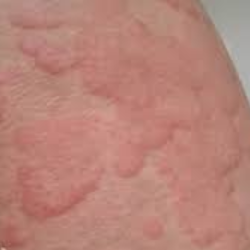
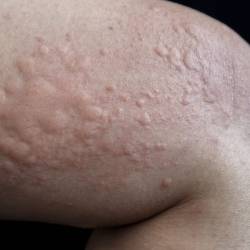
Urticaria can be classified into two main types:
Acute Urticaria – Short-lived hives that appear suddenly, often triggered by allergens, infections, or medications.
Chronic Urticaria – Persistent hives lasting more than six weeks, sometimes without a clear cause, requiring professional evaluation.
Even though urticaria is usually harmless, recurrent or severe hives should be assessed by a dermatologist to prevent discomfort and identify underlying triggers.
Urticaria arises when your immune system reacts excessively to certain triggers, releasing histamine that causes red, itchy welts on the skin. The underlying causes are often multifactorial, ranging from allergens and infections to environmental and internal health factors. Understanding these triggers can help in managing and preventing hives effectively.
Foods like nuts, shellfish, eggs, certain medications, or insect bites can trigger hives in sensitive individuals.
Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections may provoke acute urticaria episodes.

Exposure to extreme heat, cold, sunlight, or emotional stress can lead to hives.

Autoimmune disorders such as lupus, thyroid diseases, or other systemic conditions can contribute to chronic urticaria.
Urticaria can be managed successfully with a combination of medical treatments, topical care, and lifestyle adjustments. The right approach depends on the severity, frequency, and underlying causes of the hives. Consulting a dermatologist ensures that you receive a personalized treatment plan for faster relief and long-term management.
Urticaria Medication: Antihistamines, corticosteroids, or biologics like omalizumab can help control severe or chronic hives.
Topical Treatments: Cooling creams, lotions, or calamine-based products soothe itching and reduce redness.
Lifestyle Modifications:Identifying and avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods, medications, or environmental factors, is essential for preventing flare-ups.
With the right combination of treatment and trigger management, most individuals can achieve relief from urticaria and improve their skin comfort and overall quality of life.

While mild hives can sometimes resolve on their own, persistent, recurring, or severe urticaria warrants professional attention. Timely consultation with a dermatologist ensures proper diagnosis, prevents complications, and provides effective relief from itching, redness, and discomfort.
Seek treatment if hives last more than a few days without improvement.
Consult a dermatologist when urticaria keeps reappearing or occurs frequently.
Visit a specialist if the hives are accompanied by swelling of lips, tongue, or throat.
Seek immediate medical help if urticaria triggers difficulty in breathing or dizziness.
Professional guidance is advised if over-the-counter medications fail to control symptoms.
Early intervention can help manage urticaria effectively, reduce discomfort, and prevent flare-ups, allowing you to regain healthy, itch-free skin.
Get in touch with our experienced dermatologists at Wizderm to understand the cost and details of personalized urticaria treatment plans. Our specialists will design a package tailored to your skin type, severity, and lifestyle, ensuring effective and long-lasting relief from hives.
Book Your Consultation
Urticaria, also known as hives, can be uncomfortable, itchy, and disruptive, but effective treatment is within your reach. With advanced dermatological care, including antihistamines, corticosteroids, and personalized treatment plans, recurring hives can be managed and controlled. Don’t let Urticaria affect your daily life—consult an expert dermatologist at Wizderm today and take the first step towards clear, healthy, and itch-free skin!
- Reviewed by

Dr. Abhishek De Senior Consultant Dermatologist