In this Article
Male Pattern Baldness Today: What’s Changed?
Stage 1 Of Male Pattern Hair Loss: The Calm Before the Storm
Stage 2 Of Pattern Baldness in Men: The Temple Recession
Stage 3 Of Pattern Baldness in Men: Recession Becomes Reality
Stage 4: Crown Thinning Begins
Stage 5: When Front and Crown Connect
When to Seek Professional Help?Stage 6 & 7: The Advanced Phases
The 7 Stages of Male Pattern Baldness and How to Treat Them

Male Pattern Baldness Today: What’s Changed?
Stage 1 Of Male Pattern Hair Loss: The Calm Before the Storm
Stage 2 Of Pattern Baldness in Men: The Temple Recession
Stage 3 Of Pattern Baldness in Men: Recession Becomes Reality
Stage 4: Crown Thinning Begins
Stage 5: When Front and Crown Connect
When to Seek Professional Help? Stage 6 & 7: The Advanced Phases
Male Pattern Baldness Today : What's Changed?
Noticing your hairline creeping back or a widening part in your crown can spark a quiet panic. You may find yourself googling hair loss remedies at 2 AM, zooming in on old photos, or avoiding certain hairstyles. The truth is, male pattern baldness (MPB), also known as Male Androgenetic Alopecia, is incredibly common. According to NCBI, by the age of 50, nearly 30-50% of men will experience some form of it.
But here’s the good news: It can be managed.
Today’s understanding of Male Androgenetic Alopecia has come a long way from outdated myths and miracle oils. Male pattern baldness shows to follow a predictable pattern, and we can track its progression using the Norwood Hamilton Scale, a 7-stage system that shows how hair loss evolves; from barely-there changes to advanced thinning.
This article will walk you through all 7 stages of male pattern hair loss, and what to do at each one.
Stage 1 of Male Pattern Hair Loss : The Calm Before the Storm
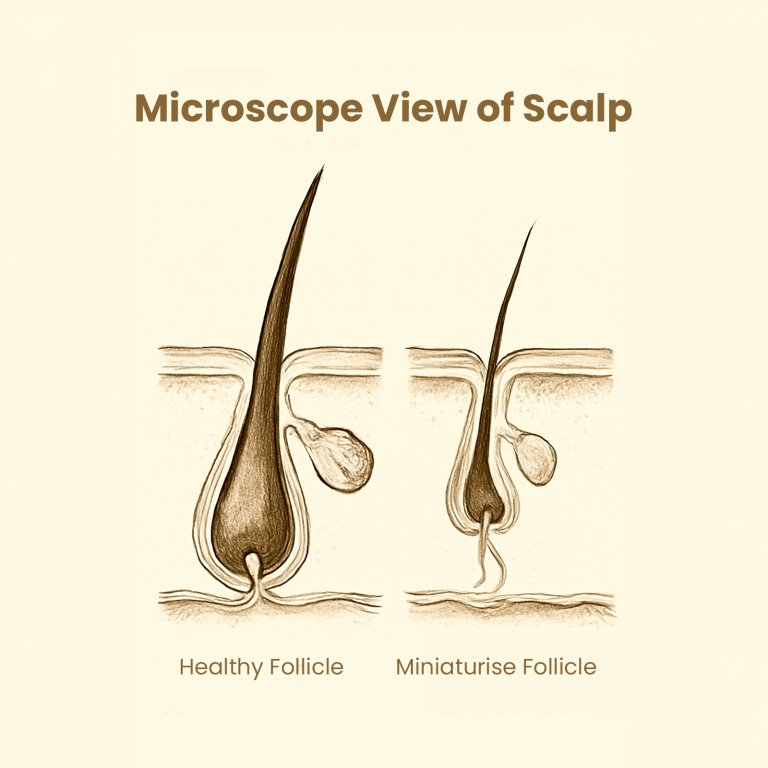
At Stage 1 of the Norwood Scale, there is no obvious hair loss to the untrained eye. The hairline looks intact, the crown seems full, and most men don’t suspect anything is wrong. But this is where early signs of Androgenetic Alopecia in men quietly begin.
While visually unnoticeable, internal changes may already be in motion. Hair follicles, especially along the frontal hairline and crown, may start miniaturizing due to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone known to shrink follicles over time in genetically susceptible men.
According to Dr. Jerry Shapiro, Professor of Dermatology at NYU Langone Health,
Hair loss begins before it’s visible. By the time patients notice recession or thinning, up to 50% of the hair in that area may already be miniaturised.
What Is Happening At Stage 1?
- Hair follicle sensitivity to DHT begins to increase.
- The growth phase (anagen) may start to shorten, while the resting phase (telogen) gets longer.
- Some men may notice more hair shedding in the shower, hairbrush, or pillow—even if the hairline looks unchanged.
Early Clues to Watch For
Increased daily hair shedding (more than 100 strands/day).
Feeling like your hair is getting “lighter” or less dense.
Dry, itchy, or inflamed scalp—sometimes the result of stress or poor scalp health accelerating hair loss.
Noticeable widening of part lines (especially visible under bright light or wet hair conditions).
What You Can Do at Stage 1?
Get a trichoscopy or scalp imaging scan to detect early follicular miniaturization.
Start preventive scalp care: caffeine-based shampoos, DHT-blocking ingredients like saw palmetto, and salicylic acid for buildup removal.
Focus on nutrition (iron, vitamin D, omega-3s) and reduce chronic stress, both of which are strongly linked to telogen effluvium and DHT sensitivity.
Stage 2 of Pattern Baldness in Men : The Temple Recession
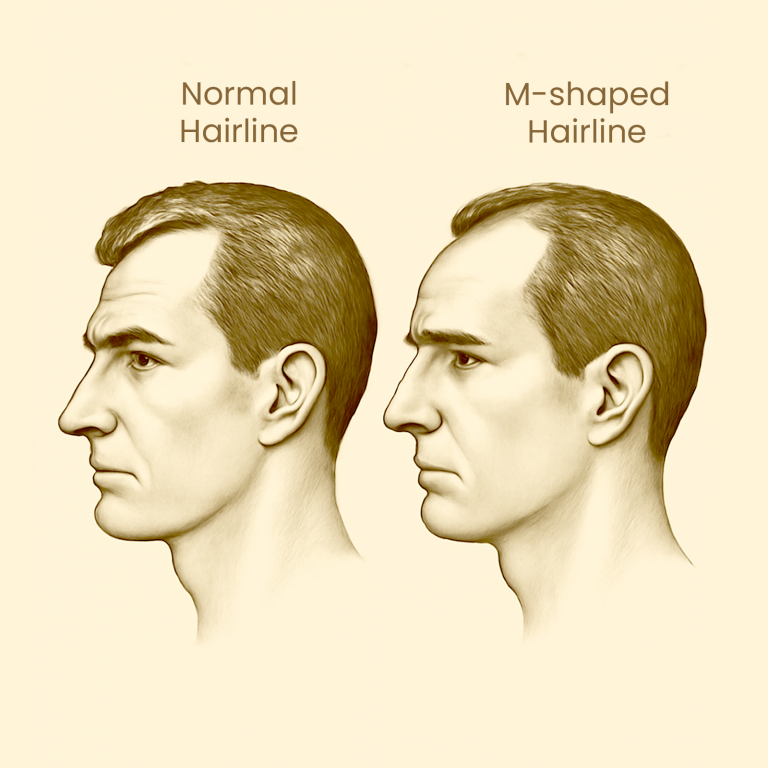
This is where male baldness begins to leave visible clues. At Stage 2 on the Norwood Scale, there is noticeable thinning or recession at the temples, typically forming the earliest signs of an “M-shaped” hairline. The central hairline may still appear stable, but the corners are beginning to recede. This stage is still considered mild, but it’s a turning point—a signal that the underlying hair loss process is accelerating.
Psychological Impact - False Confidence and Missed Opportunity
Since the overall hair density may look normal, many men tend to avoid going to the doctors. They also start extensively using over-the-counter remedies. Some would simply ignore the signs until it gets worse.
Stage 3 Of Pattern Baldness in Men: Recession Becomes Reality
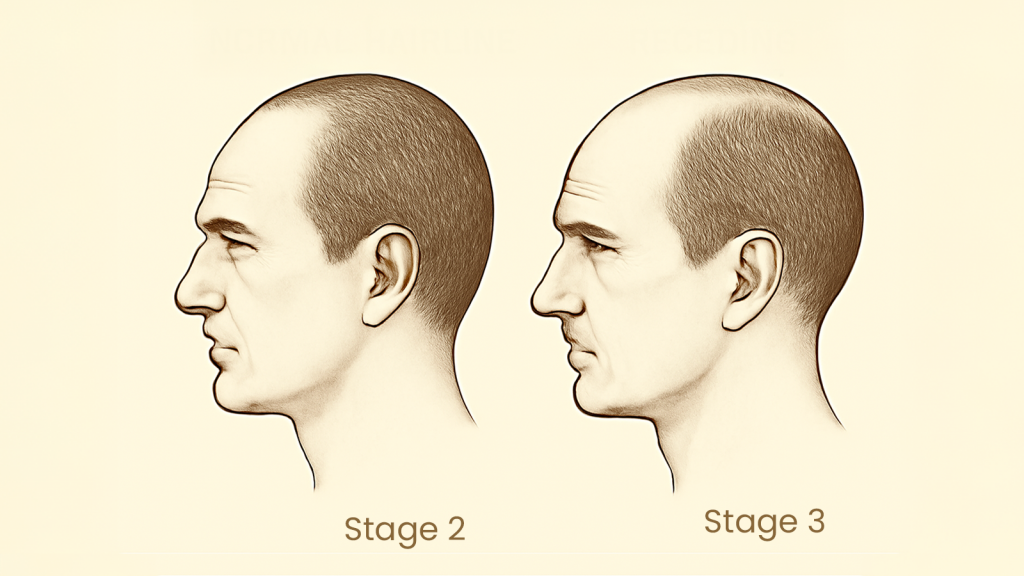
At Stage 3, male pattern baldness becomes visibly noticeable to others. The M-shaped hairline deepens with more pronounced temporal recession, and for many men, this is the first point where denial starts to fade and concern becomes real.
According to dermatologists, this is the most common stage at which Indian men seek clinical help, often after trying home remedies or cosmetic cover-ups that haven’t worked.
What Are The Treatment Options For Baldness At This Stage?
-
Minoxidil
Topical minoxidil (2%-5%) is an FDA-approved drug and is easily available in India. Minoxidil helps in increasing blood flow to the hair follicles. It also helps in extending the growth phase and helps maintain hair density.
-
Finasteride
Finasteride blocks the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to DHT. Finasteride is clinically proven to slow hair loss and promote hair regrowth.
What is Happening on the Scalp?
At this stage, the follicles at the temples are now significantly miniaturised, producing thinner and weaker hair that is more likely to fall out. The central hairline may also start moving backwards, though the crown usually remains intact at this point. This is when men start noticing:
- Their forehead appears broader
- Hair doesn’t hold volume like before
- Hairline looks uneven or patchy in photos or under harsh light
What you can do at Stage 3 of Androgenic Male Alopecia?
- Stick to Proven Treatments
At this point, you should only stick to proven treatments but intensify the dosage. The Topical Minoxidil dosage should be upped to 5% and used consistently. Pair with microneedling once or twice a week to increase absorption and stimulate dermal papilla cells. You can also consider using Duasteride in a low dose if Finasteride has not worked for you. This should be under complete dermatologist supervision.
- Start Scalp Health Optimization – Use a salicylic acid or ketoconazole shampoo 2-3 times a week to reduce inflammation, oil buildup, and microflora imbalance. Avoid heavy oils and pore-blocking products. Keep your scalp clean, nourished, and hydrated at this stage.
Stage 4 : Crown Thinning Begins
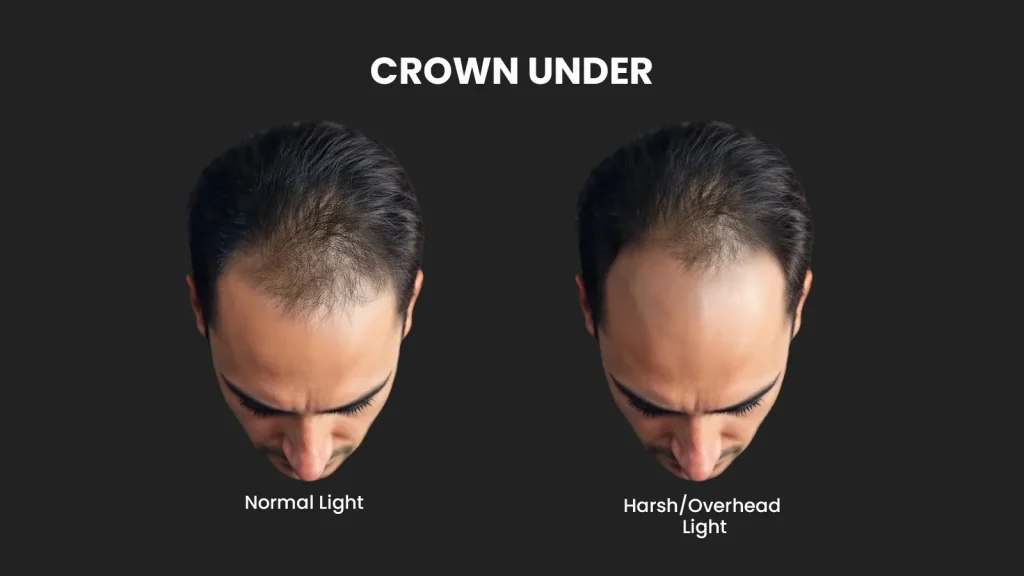
If you’re noticing your scalp peeking through the top of your head, especially under overhead lighting or in photos, you’re likely entering Stage 4 of male pattern hair loss. At this stage, your hairline continues to recede, but the real game-changer is what happens at the crown (also known as the vertex). This is when two previously separate zones: your temples and the crown, start showing noticeable thinning, and for many men, that’s when the alarm bells ring.
Crown Hair Thinning : Why It's So Tricky ?
Unlike frontal recession, which is easier to spot in the mirror, crown thinning often goes unnoticed until it becomes significant. The hair at the crown tends to thin in a circular or spiral pattern, gradually expanding outward. Because the crown is difficult to see without mirrors or photos, many men don’t realise they’re losing hair there until the area is already advanced.
What is Happening In Stage 4?
- Follicles in both the frontal hairline and crown are now affected by DHT (dihydrotestosterone).
- Miniaturised hair strands are shorter, finer, and have a shorter growth cycle.
- The “bridge” of hair between the front and crown still exists—but it’s starting to narrow.
Hair Loss Treatment at Stage 4 : Be Strategic
At this point, treatment needs to be multi-modal; a single product or supplement won’t reverse crown hair thinning alone.
-
Topical Minoxidil (5%)
Minoxidil is particularly effective at encouraging regrowth on the crown. This product should be applied twice daily, as consistent use is essential for visible results. Choosing a spray or foam format can help achieve more even coverage across the crown area.
-
Oral Finasteride or Dutasteride
Formulated with proven DHT blockers that can slow or halt hair loss at both the hairline and crown, treatment often begins with Finasteride, while Dutasteride may be considered off-label for stronger control. Noticeable improvement usually appears within three to six months of consistent use.
-
Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Devices like laser combs and helmets help in stimulating the blood flow and ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) in follicles. ATP production is the main part that helps in the normal hair growth cycle and hair shaft formation. LLLT is especially beneficial for widespread thinning of the crown.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
Hair PRP treatment involves injecting your own growth factors on the scalp to stimulate inactive follicles. It also works well with oral and topical medication.
Stage 5 : When Front and Crown Connect
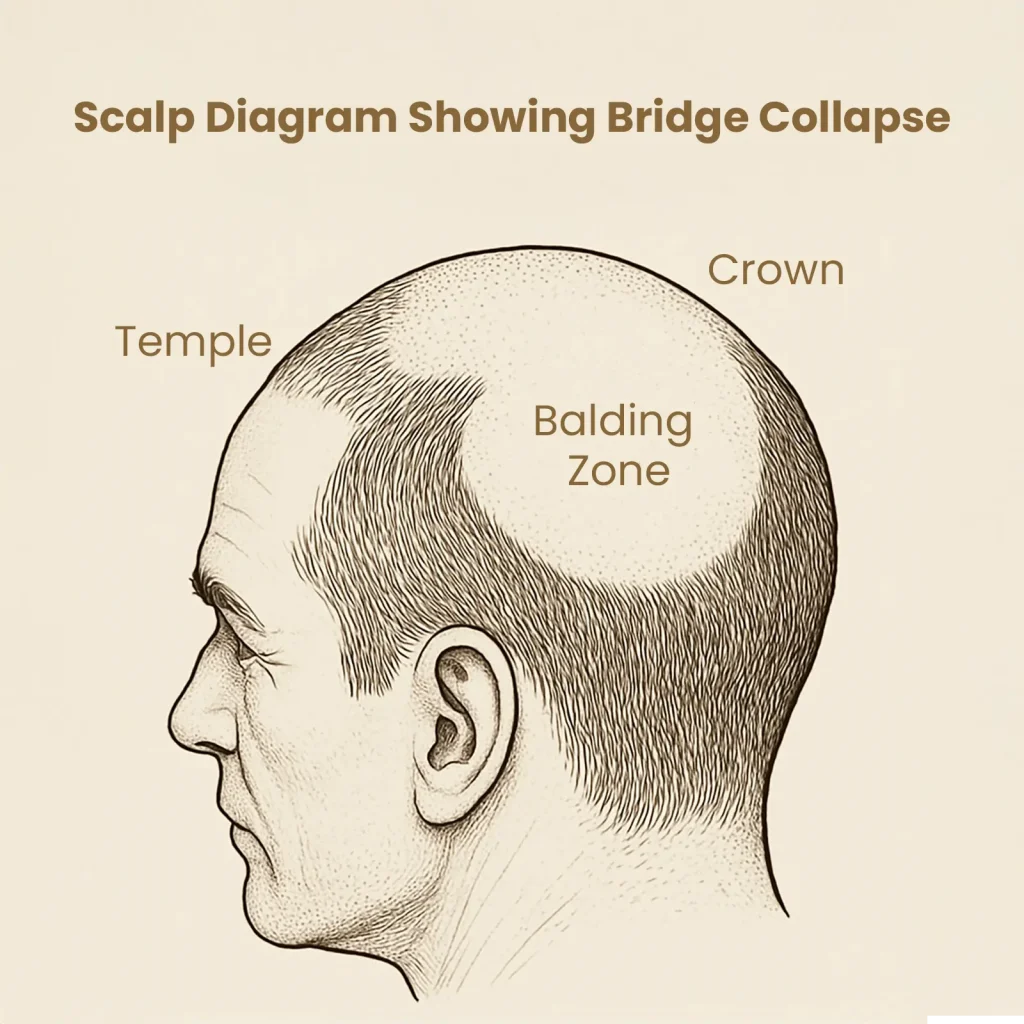
Stage 5 marks a critical turning point in male pattern hair loss—this is where the once-separate areas of hair loss at the frontal hairline and crown begin to merge. The “bridge” of hair that previously separated the two zones starts to thin out or vanish completely, leading to a large balding area across the top of the scalp. This is often when men begin seriously exploring medical intervention or hair restoration options
What's happening on the Scalp in Stage 5?
- The anterior hairline recession and crown thinning are now visibly connected.
- The remaining hair in the “mid-scalp bridge” is sparse, weak, and prone to shedding.
- Hair on the sides and back (the occipital and parietal regions) usually remains intact, forming the classic “horseshoe” pattern of baldness.
This is considered the beginning of advanced male pattern baldness.
What are the treatments for Baldness At Stage 5?
At this stage, regrowth becomes more challenging but not impossible—especially with the right mix of therapies. However, expectations need to be realistic. Most results aim to improve density and prevent further loss rather than restore a full head of hair without surgical support.
Oral Finasteride / Dutasteride
At stage 5, Dutasteride or Finasteride is essential to stop further miniaturisation of hair follicles. Although Dutasteride helps with deeper DHT suppression, you should use it only if it’s prescribed by a dermatologist.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) + Microneedling
PRP combined with microneedling helps stimulate dormant follicles and improve scalp health. It’s especially effective in the thinning “bridge zone,” potentially thickening weak hair. Results vary, depending on follicle viability and consistency of treatment.
Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation is the most effective long-term solution for Stage 5 hair loss. It involves relocating healthy follicles from the sides and back to bald areas. Advanced techniques like FUE and DHI provide natural, lasting results with proper post-op care.
Stage 6 & 7 : The Advanced Phases :
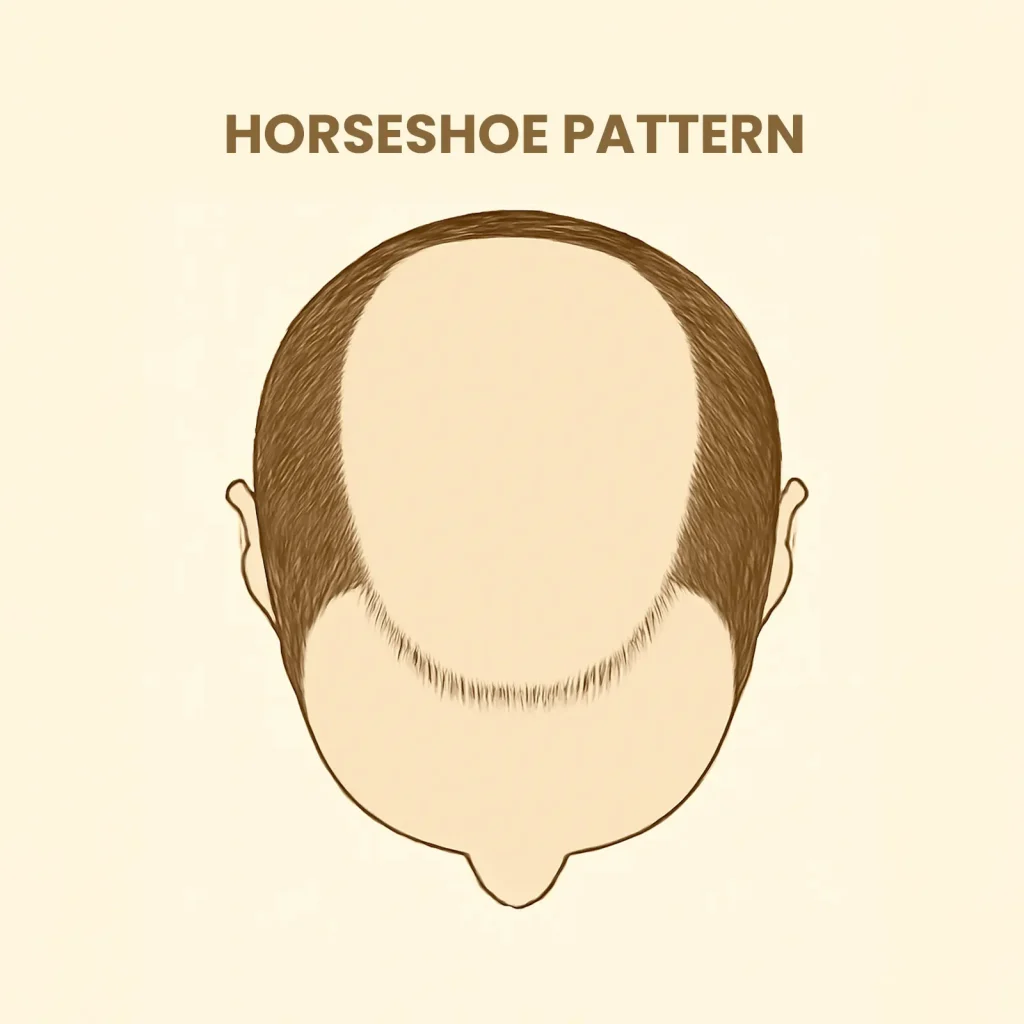
By the time a man reaches Stage 6 or 7 of male pattern baldness—also known as advanced androgenetic alopecia for men—most of the top of the scalp is bare. What remains is a rim of hair around the sides and back of the head, forming what is famously referred to as the “horseshoe pattern.”
At this stage, the battle is no longer about preventing hair loss—it’s about deciding how to live with it, restore it, or redefine your look altogether.
Understanding the Horseshoe Pattern
The horseshoe-shaped rim of hair (also known as the occipital and parietal fringe) is often resistant to DHT, which is why it remains even when the crown, front, and mid-scalp have gone completely bald. But this remaining hair often thins in density too, and the scalp becomes fully visible under light.
What’s Really Happening in Stage 6 & 7 of Male Androgenic Alopecia?
The front and crown have merged, forming a single, large bald area across the scalp.
The bridge of hair in the mid-scalp is gone or extremely sparse.
Hair loss on the sides and back may creep higher, especially in Stage 7.
Scalp health declines, with lower blood flow and reduced follicular activity.
Treatment Options: What Can You Really Do at Stage 6 & 7?
Hair Transplant Surgery (with Limitations)
Hair transplant surgery is an option for advanced hair loss, but it comes with limitations due to the finite donor area—typically the sides and back of the scalp. This restricted supply of healthy follicles means full coverage, especially for extensive balding, may not be achievable. Instead, the realistic goal becomes creating a natural-looking hairline or partially restoring density in strategic areas to frame the face and improve overall appearance. Techniques like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) are commonly used, though patients may require multiple sessions to achieve desired density and coverage.
Where are you , and Where Do You Want to Go?
Maybe it’s just a receding hairline. Maybe the crown is starting to thin. Or maybe you’re already seeing that classic horseshoe pattern. No matter which stage of male pattern baldness you’re in, there’s always a path forward.
At Wizderm, we don’t believe in one-size-fits-all treatments. Our expert dermatologists use a stage-specific, root-cause-based approach to assess your condition and create a personalised plan; whether that involves minoxidil, oral finasteride, non-hormonal innovations, or hair restoration procedures.
Final Notes from Wizderm
Hair loss is personal, and so is the journey to treat it. As we’ve seen through the 7 stages of male pattern baldness, early awareness and timely action can make a significant difference in long-term outcomes.
Whether you’re just noticing a few extra strands on your pillow or you’ve already reached an advanced stage, know this: you’re not alone, and you’re not without options.
Wizderm combines medical expertise, evidence-based treatments, and genuine care to help you feel confident in your scalp and yourself. Because hair might be what’s falling; but self-worth never should.
Visit your nearest Wizderm clinic today and take the first step toward stronger, fuller, healthier hair.
FAQs
Can male pattern baldness grow back?
Yes, male pattern baldness can be slowed down and partially reversed, especially in the early stages. Treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, and newer non-hormonal options can regrow hair in thinning areas, but completely restoring lost hair in advanced stages is unlikely without procedures like hair transplant. Early intervention is key
Can you fix male pattern baldness?
Male pattern baldness can be managed but not completely cured. Treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, PRP, and hair transplants can slow hair loss and restore some growth. Early intervention offers the best results, but full regrowth is rare. Maintenance is key to preserving and optimizing outcomes over time.
Is balding at 25 normal?
Yes, balding at 25 is relatively common. Male pattern baldness can begin as early as the late teens or early 20s due to genetics and hormonal factors. Early signs like a receding hairline or crown thinning are typical, and starting treatment early often leads to better results.
Do hair loss tablets work?
Yes, hair loss tablets like finasteride can be effective for many men. They work by blocking DHT, a hormone that shrinks hair follicles. This can slow hair loss and even regrow hair in some cases. However, results vary, and consistency is key, but, potential side effects should be considered
Is a hair transplant permanent?
Yes, a hair transplant is generally considered permanent. The transplanted hair follicles, taken from the sides or back, are genetically resistant to balding and typically continue to grow for life. However, surrounding non-transplanted hair may still thin over time, so ongoing care or treatments might be needed to maintain overall density.
Why is pattern baldness more common in males?
Pattern baldness is more common in males due to higher levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. In genetically predisposed men, DHT shrinks hair follicles, leading to thinning and eventual hair loss. Women also experience pattern hair loss, but typically with less DHT sensitivity and a different pattern.
Can male pattern baldness be cured naturally?
Male pattern baldness cannot be fully cured naturally, as it’s driven by genetics and hormones (mainly DHT).
Is male pattern baldness genetic?
Yes, male pattern baldness is primarily genetic. It’s inherited from both maternal and paternal sides and is linked to sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). If close relatives have experienced early hair loss, there’s a higher chance you may too. Genetics largely determine when and how rapidly hair loss progresses







