

In this Article

Causes of hair loss can be distressing, especially since long, luscious hair is often seen as a beauty ideal. However, when you begin to fall short of that standard, understanding the root causes is the first step to taking control.
Consequently, your confidence and self-esteem may take a hit. But don’t worry—hair loss is common and occurs daily. Still, it’s important not to confuse it with hair fall. Although these terms are used interchangeably, they are not the same.
To clarify, hair loss refers to the natural shedding of 50–100 hairs per day, making room for new growth. In contrast, hair loss is a more serious condition in which the hair may not grow back, often leading to bald patches or thinning. Medically, this is known as alopecia and can be either temporary or permanent.
Therefore, in this article, we’ll explain the top 10 causes of hair loss and offer simple, effective tips to help you prevent it.

Reviewed by Dr. Harsha Sarawgi
MBBS, MD in Dermatology, Venerelogy & Leprosy
Updated on: May 17, 2025
Hair loss, or alopecia, is a gender neutral condition where you shed more hair than you can regrow. This is because of the disruption in the hair production cycle. Although hair loss can affect your entire body, you can find it mostly starting from the scalp.
There are various types of hair loss. The popular ones include:

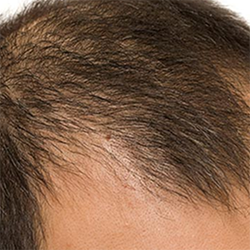
Male or female pattern baldness, medically known as androgenic alopecia, is the most common type of hair loss. This condition is largely hereditary, meaning it is passed down through generations. However, it affects men and women differently.
For instance, if you’re a man, hair loss typically begins at the temples and crown of the head. On the other hand, if you’re a woman, you’ll likely experience diffuse thinning across the entire scalp rather than distinct bald spots.
Although androgenic alopecia is more common with age, it can start any time after puberty. Moreover, hormonal changes also play a key role. As a result, women may notice increased thinning during or after menopause.
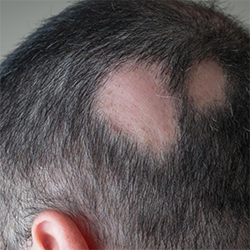
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease and one of the more severe causes of hair loss. In this condition, your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to sudden hair loss. As a result, you may notice small, round bald patches on your scalp—or in some cases, on your eyebrows.
Although the exact cause isn’t fully understood, early diagnosis is crucial. Therefore, it’s important to consult a dermatologist to explore effective treatment options and manage the condition promptly.
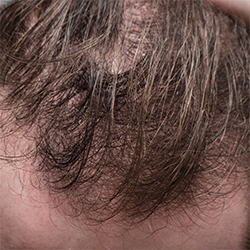
Telogen effluvium is a type of hair loss where a larger-than-normal number of hair follicles enter the resting phase (telogen). In this condition, the loss of hair is temporary. This condition is mostly linked to your emotional and physical well being, as it occurs after a few stressful months or hormonal fluctuations. Unlike other types of hair loss, Telogen effluvium typically doesn’t lead to complete baldness and is easily treatable.
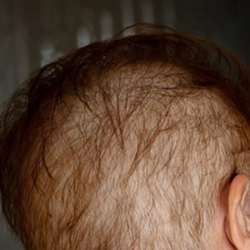
Anagen effluvium is a rapid and severe form of hair loss that occurs during the growth phase (anagen) of the hair cycle. Unlike telogen effluvium, which causes shedding during the resting phase, anagen effluvium leads to hair loss while the hair is actively growing, thereby disrupting the normal growth cycle.
This condition is primarily triggered by external factors such as:
-Chemotherapy or Radiation
–Certain Drugs or Harmful Chemicals
–Severe Infections
Traction alopecia is a condition where hair loss occurs due to intense hair pulling leading it to break away. This kind of hair loss occurs due to pulling of hair by tying it up in tight buns, ponytails or hair styles like cornrows or braids.

Hair loss is more common than you think. Baldness affects almost 85% of males and 20%-30% in case of females in India itself. Almost 2% of the world population is affected by alopecia areata.
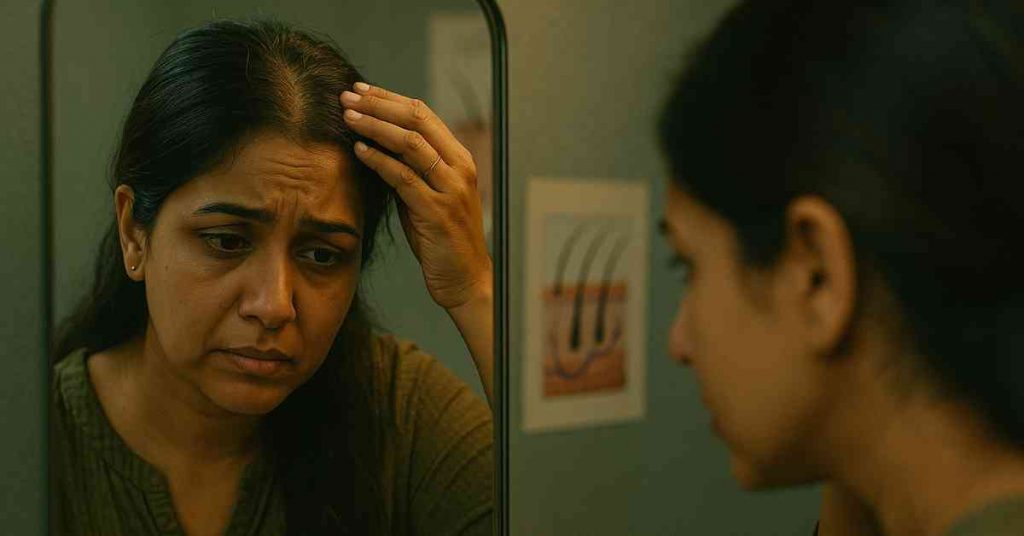

The causes of hair loss are not totally identified yet, but some of the main causes of hair loss include:
Genetics are one of the most important causes of hair loss. Androgenic alopecia or male or female pattern baldness is mainly driven due to genetic predisposition and sensitivity to DHT or dihydrotestosterone (a hormone which stimulates hair growth).
Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome, pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders (hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism) can disrupt the hair growth cycle. This can lead to hair thinning or shedding. Post-partum hair loss is a common example where hormonal fluctuations after childbirth cause noticeable hair fall.
Physical stress and emotional distress can push a large number of hair follicles into resting (telogen) phase prematurely.
Ageing slows the process of hair growth. At a certain point, the hair follicles stop growing, leading to hair thinning or receding hair line.
Poor diet and lack of proper nutrients leads to hair loss. Nutrients like zinc, vitamin D, biotin, and protein are the key components of hair growth. Without these nutrients, the hair becomes brittle and breaks off easily.
Auto-immune disorders like alopecia areata, where the hair follicles are mistakenly attacked by your immune system. This leads to patchy baldness in our hair.
Treatments like chemotherapy or radiation can damage your hair rapidly by dividing cells. This causes sudden, widespread hair loss. Medications like antidepressants, blood thinners and beta blockers result in diffuse thinning.
Inflammatory scalp conditions like psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis and fungal infections like ringworm can severely damage the scalp’s environment. This leads to disrupted hair growth, weakened hair growth, or patches of hair loss.
Tight hairstyles like braids and ponytails pull out the hair from its roots. If this is continued there is irreversible damage to the scalp. Same goes for colouring hair or bleaching it.
Pollution, humidity, sun exposure impacts scalp health, production of natural oil production of our hair, and disrupts hair growth. All of these factors result in slow or no regeneration of hair, causing hair loss.
Symptoms of hair loss are easily identified. The most common ones are right in front of your eyes. Those include:
You cannot completely stop the process of hair loss but you can definitely slow it down. Here are some easy ways you can prevent hair loss:
If you start noticing persistent hair loss or patchy baldness, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist without delay. Such conditions require expert evaluation and personalized treatment. Fortunately, one of the best clinics in town you can trust is Wizderm Skin and Hair Clinic.
At Wizderm, advanced hair treatments are not only effective but also convenient and painless. So, as soon as you observe the symptoms of hair loss, simply book a consultation — and take the first step towards healthier hair!
Yes, absolutely! It is very important to destress yourself every day to help reduce hair loss. You can try various destressing methods, such as aromatherapy, meditation, and more, to calm both your mind and body.
The best way to determine if your hair loss is hereditary is to look for signs of similar hair loss in the older generations of your family.
Most of the time, over-the-counter products are highly effective for managing hair loss. However, in severe conditions like alopecia areata, professional dermatological intervention becomes necessary.
You don’t necessarily need to make drastic changes to your diet—unless you frequently consume junk food. Instead, focus on maintaining a healthy and clean diet to support your hair health.
In this Article
Hair Loss in Men and Women: The Basics
Hair Loss in Men: The Usual Suspects
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness
Treatment Options for Male Hair Loss
Hair Loss in Women: A Different Beast
Causes of Female Pattern Hair Loss
Treatment for Female Hair Loss
Common Ground for Both the genders
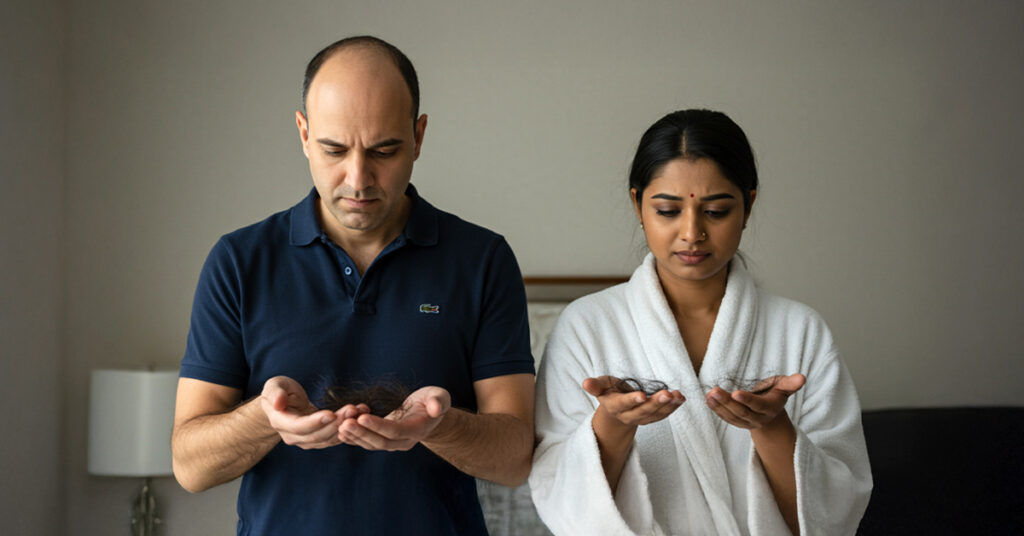

Let’s face it: Hair loss is a universal concern.
Whether you’re a man noticing a receding hairline or a woman spotting thinning locks, the emotional toll can be significant.
But here’s the kicker—male and female hair loss aren’t the same. The patterns, causes, and treatments vary widely. That’s why understanding these key differences can make all the difference in finding a solution that truly works for you.
So, are you ready to unravel this hairy mystery?

Reviewed by Dr. Harsha Sarawgi
MBBS, MD in Dermatology, Venerelogy & Leprosy
Updated on: March 10, 2025
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s lay some groundwork. Hair loss—scientifically known as Alopecia—affects millions of people worldwide. In most cases, the usual suspect for men is male pattern baldness, formally known as Androgenetic Alopecia. Women, on the other hand, often face a broader range of triggers, including hormonal imbalances, chronic stress, or even hairstyles that put excessive tension on their strands.
While men typically notice a receding hairline or thinning at the crown, women usually experience diffuse thinning across the entire scalp. Think of it this way: for men, it’s like an entire drawer of socks vanishing overnight. For women, it’s one sock here, another there—until the whole collection feels suspiciously light.
The infamous male pattern baldness—officially known as androgenetic alopecia—is the most common type, affecting up to 70% of men at some point in their lives.
Typically, the hallmark sign is a receding hairline that slowly morphs into a horseshoe-shaped pattern of hair around the crown.
While classic, this pattern is definitely not what anyone hopes for.

Blame it on your genes and hormones.
In most cases, male pattern baldness is primarily caused by a sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone.
So, How Does This Work?
DHT gradually shrinks hair follicles, making it harder for new hair to grow. As a result, hair strands become thinner and shorter over time. Eventually, the follicles stop producing hair altogether. In other words, it’s a bad hair day that can last for years!
Of course, other factors like stress, poor nutrition, and certain medical conditions can worsen hair loss in men. However, DHT is usually the main culprit.
The good news?
Science has your back. Here are some effective treatments:
Minoxidil: A topical treatment that stimulates hair growth. Bonus: It’s available over the counter.
Finasteride: An oral medication that reduces DHT levels. A doctor’s prescription is required, though.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) can restore your hairline,
though these are more invasive and pricey options.
Improving your Diet, Managing Stress, and Avoiding Harsh Hair Treatments can help slow down hair loss.
For women, hair loss is less about receding hairlines and more about overall thinning. In fact, female pattern hair loss—the female counterpart to androgenetic alopecia—affects about 40% of women by the age of 50. Unlike men, women rarely go completely bald. Nevertheless, that doesn’t make the experience any less distressing.
Hormones play a big role here, too. Estrogen helps keep hair in its growth phase, but when estrogen levels drop—like during menopause—female loss of hair often kicks in. Other culprits include:
Women have their own set of solutions to combat female pattern baldness:
Minoxidil: Yes, it works for women too! Look for a 2% or 5% formula.
Birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy can help balance hormones and reduce hair loss in some women.
Supplements like Biotin, Iron, and Zinc can support hair health.
Don’t forget a balanced diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, and lean proteins.
Devices like Laser Combs or Caps can stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
In rare cases, women experience a male form of baldness (a receding hairline or crown thinning). Treatments like Finasteride are sometimes prescribed off-label for women but require careful medical supervision.

The Good News?
Conversations about hair loss are becoming less taboo. Nowadays, celebrities, influencers, and everyday people are sharing their stories—whether they’re rocking wigs or proudly showing off their bald heads. As a result, the more we normalize it, the less isolating it feels.
For example, Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson and Jada Pinkett Smith have openly embraced their journeys, proving that hair loss doesn’t diminish star power. Ultimately, it’s a reminder that confidence shines brighter than any hairstyle.
If you’ve tried over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes but your hair loss still persists, then it might be time to seek professional help. After all, hair loss can sometimes indicate underlying issues such as thyroid imbalances, autoimmune diseases, or nutrient deficiencies.
Therefore, consulting a dermatologist can help you pinpoint the root cause and develop a tailored treatment plan.
Looking for Expert Care?
Wizderm Skin and Hair Clinic, a leading dermatology clinic, specializes in treating hair loss in both men and women.
With advanced diagnostics and personalized care, they’ll help you regain not just your hair—but your confidence. So why wait? Book an appointment today.
Hair loss in men and women may differ in both cause and treatment, yet the emotional journey is something we can all empathize with. Whether you’re battling thinning strands or embracing a shiny dome, remember this: Hair doesn’t define you. What truly matters is how you carry yourself—with or without it.
So, here’s to keeping your head held high. And whether it’s covered in hair, a hat, or just a generous dose of sunscreen, may it always be fabulous.
For men, hair loss is most commonly caused by androgenetic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness. This condition is linked to genetics and hormones like DHT (dihydrotestosterone). In contrast, for women, the causes are more varied, including hormonal changes—such as pregnancy and menopause—stress, nutritional deficiencies, and certain hairstyles that put stress on the scalp.
It’s normal to lose 50–100 hairs per day. However, if you notice sudden or excessive shedding, patchy bald spots, or a receding hairline, then it’s worth consulting a dermatologist to rule out any underlying conditions.
Yes, Minoxidil is a topical treatment approved for both men and women to stimulate hair growth. On the other hand, Finasteride is an oral medication effective for men, as it targets DHT. However, women should avoid Finasteride unless explicitly advised by a doctor.
While lifestyle changes may not completely stop hereditary hair loss, they can help slow its progression. For instance, eating a nutrient-rich diet, managing stress, avoiding excessive heat styling, and practicing proper scalp care can make a noticeable difference.
If over-the-counter (OTC) treatments don’t yield results, then it’s important to consult a dermatologist. They can diagnose the root cause of your hair loss and suggest advanced options such as prescription medications, low-level laser therapy, or even hair transplants.
Registered Office
Wizderm Speciality Skin & Hair Clinic 1/503, Gariahat Road, Jodhpur Park, Kolkata, West Bengal 700068
Mon - Sat: 10 AM - 8 PM
© 2025 Wizderm Speciality Skin & Hair Clinic. All rights reserved.
Crafted with by Auraveni Solutions.
Stay updated with expert tips, latest treatments, and exclusive offers. Subscribe to Wizderm's newsletter for healthy, glowing skin and hair!